Basic functions of the CLARIN metadata infrastructure (CMDI).
This will describe the basic functions of the CMDI being faithful to what was presented at different occasions.
1. Allowing users to create adequate metadata descriptions.
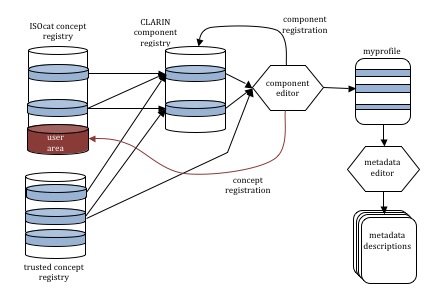
The user is presented a GUI where he can compile an adequate metadata schema for a metadata description by selecting metadata components from a so called "metadata component registry". These components all are supposed to describe a particular aspect of a resource. For instance an "ActorLanguage?" component will describe all relevant aspects of a language available to an actor. Another component "Location" may describe relevant aspects of a region or town that a researcher finds useful to describe, as where e.g. a recording took place. Such components can be aggregated into a single metadata description. To overcome problems with semantic interoperability every metadata element in a component has to have a reference to a concept registry as do the components as a whole.
Users must also be able to create their own components either on the basis of aggregating existing components into new ones, or by defining completely new ones as long as the elements have references to an accepted concept registry. It has always been clear that we need to seed the initial component registry with components taken from the existing metadata sets so that we can achieve interoperability with the huge existing installed base of metadata descriptions such as those of IMDI, OLAC, TEI, etc. Determining the set of CLARIN interoperable metadata sets is political sensitive; every such set will require resources.
When the user has created a selection of components, such a selection can be saved for future use in the form of a metadata profile that can be exported as an XML-schema (different flavors are possible). Within the CMDI there will be simple GUIs available to fill-in every component in the component registry. But the schema can be used to work with tools outside the CMDI.
2. Harvesting available CLARIN metadata descriptions
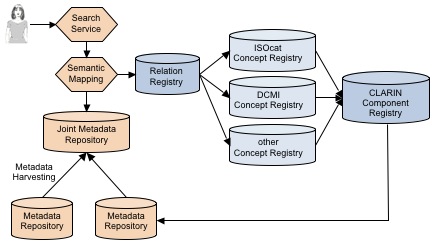
The second major function of the CMDI is to harvest available metadata descriptions and store them into central metadata element repositories. In CLARIN only suitable offerings of metadata are accepted, those that use metadata components whereof all elements have references to accepted concept registries. Such metadata element repositories should offer a metadata search & browsing service to the user community.
3. Metadata Search & Browsing Service
The metadata search service & browsing is offered to users via (1) a GUI allowing users to create queries on the basis of the elements and vocabularies available in the repository and (2) a web service. The service can make use of the references to the concept registry and relation registries to make different components interoperable if their semantics overlap. It is at this moment not clear if this should be implemented by having a semantic normalization step before storing the metadata descriptions in the repository or (as is depicted in the figure) having a translation of a metadata query into different component-specific ones. The first possibility places more emphasis on correct description and being able to retrieve that description using a familiar vocabulary and while the second places more emphasis on harmonizing all semantic content by having a well chosen normalized vocabulary. (As discussed in Nijmegen 2009-05-14, metadata must be stored in the CmdiRepository as provided by the metadata providers. Any semantic mapping will be the sole competency of CmdiRelationRegistry used by CmdiMetadataServices when resolving/expanding queries.)
This text is derived from the CLARIN EU WP2 workdocument: CLARIN metadata infrastructure
Attachments (2)
- CMDIoverview1.jpg (33.0 KB) - added by 15 years ago.
- CMDIoverview2.jpg (30.7 KB) - added by 15 years ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip